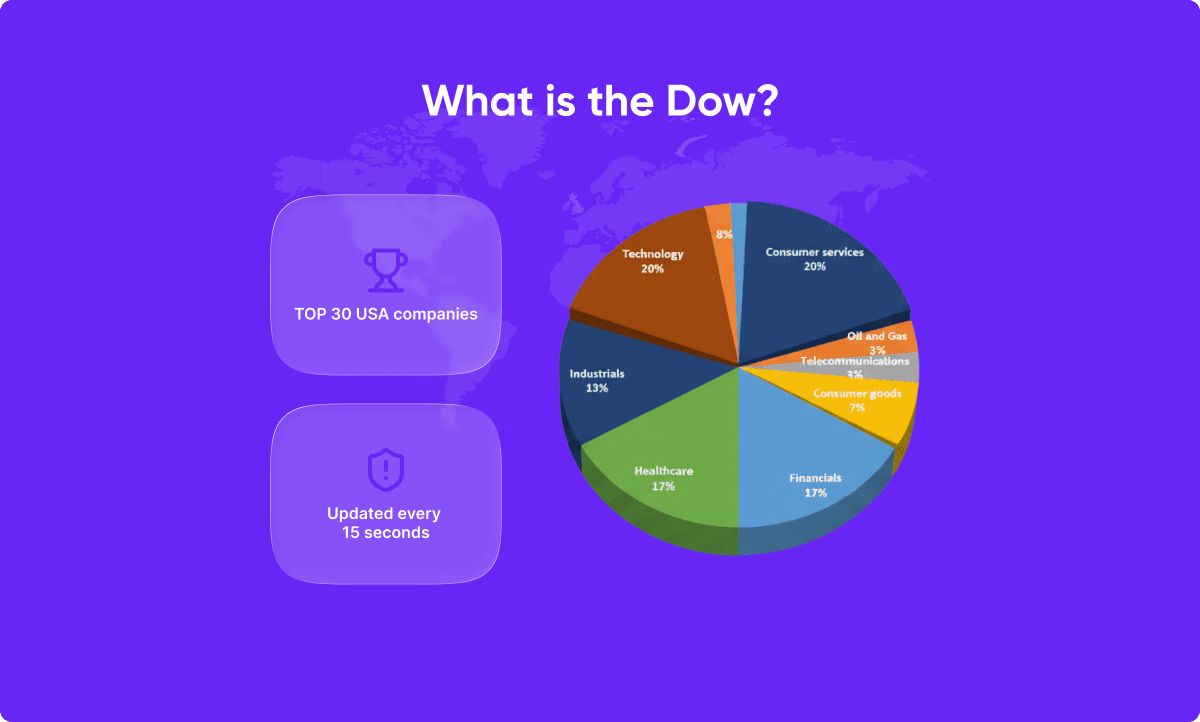
The Dow, or the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), is a major price-weighted index tracking 30 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States. The Dow has been in existence for more than a century and was first published on May 26, 1896. It remains one of the world’s most recognized financial benchmarks, providing a measure of the overall health of the U.S. economy.
As the oldest U.S. stock market index, the Dow is not only a gauge of major U.S. company performance but also a reflection of investor confidence in the world’s largest economy. The Dow’s movements have a significant influence on global markets and related instruments. It is closely watched by economists and investors around the world, serving as one of the most closely monitored indicators of market sentiment.
Many traders learn How to Trade the Dow Jones Index to gain exposure to U.S. market movements without needing to buy individual stocks, often through modern platforms or brokers.
The Dow is often used as a benchmark for other indices, such as the S&P 500 and the NASDAQ. Although each index has different weighting methods and categories of stocks, they all provide insight into the relative performance of U.S. stocks. In addition, when the Dow moves up or down, it often reflects overall market sentiment, earning it the nickname “the global market barometer.”
The Dow is composed of 30 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States. The components are chosen by the Editors of The Wall Street Journal, representing the most significant and influential sectors of the U.S. economy.
Examples of Dow constituents include Apple, Boeing, Goldman Sachs, Johnson & Johnson, McDonald’s, Microsoft, and Walt Disney, each representing a key industry segment.
Because the Dow is price-weighted, stocks with higher share prices exert greater influence on index movements, regardless of company size or market capitalization.
For investors using a trusted stock trading broker, the Dow often serves as a benchmark for comparing portfolio performance and assessing exposure to U.S. equities.
The Dow is calculated using a price-weighted average formula. This means the total of all 30 component prices is divided by a figure known as the “Dow Divisor.”
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how the Dow works:
The Dow Divisor changes over time to account for stock splits, company replacements, or structural adjustments, ensuring continuity in the index’s value. The Dow is recalculated every 15 seconds during trading hours based on the latest trade prices, providing near-real-time updates for investors and traders.
The DJIA is a price-based index and is not adjusted for inflation, although many other stock market indexes are. This means that the value of the Dow moves with the prices of stocks rather than reflecting changes in a company’s fundamental value.
Today, traders can access the Dow via advanced indices trading app platforms, making it easier to monitor market changes and execute trades instantly.
The Dow and the S&P 500 are two of the most widely followed U.S. stock indices. The Dow tracks 30 large-cap companies, while the S&P 500 follows 500 major firms representing roughly 80% of U.S. market value.
The Dow is price-weighted, meaning the companies with the highest prices have the most influence on the Dow’s performance. The S&P 500, on the other hand, is market-capitalization weighted, meaning that each company’s influence on the index is determined by its market value rather than its share price. The Dow reflects investor sentiment in large, diversified blue-chip stocks, while the S&P 500 is seen as a more reliable and accurate measure of the stock market’s performance.
Many traders use CFD trading to speculate on both the Dow and S&P 500 movements, allowing them to profit from price changes without owning the underlying assets.
The Dow and the NASDAQ are both stock indices that track U.S. equities, but they differ significantly in their composition and weighting. The Dow contains 30 price-weighted industrial leaders, while the NASDAQ includes over 3,000 companies and is market-cap-weighted.
The NASDAQ is composed of more tech-focused companies and is seen as a more accurate measure of the performance of the tech sector. As the largest electronic stock market in the world, the Nasdaq is closely watched for insights into innovation-driven companies like Apple, Amazon, and NVIDIA.
To better understand market trends, study How to Interpret Dow Market Movements to recognise patterns, investor sentiment, and broader economic signals.