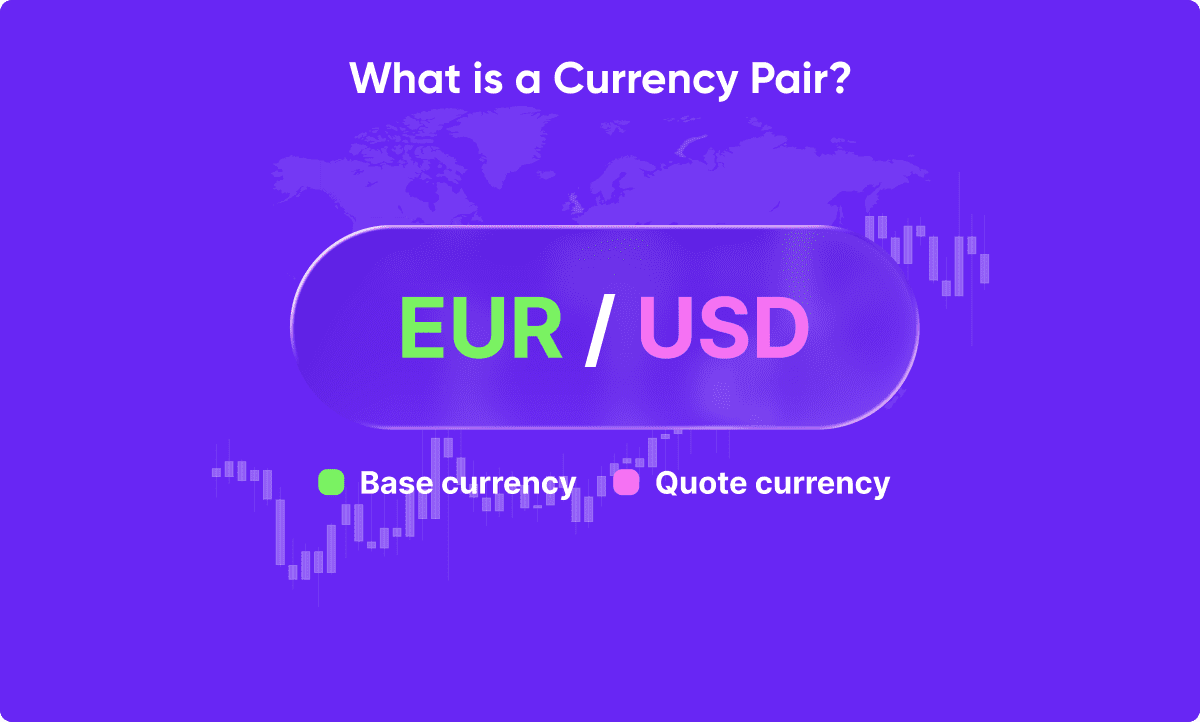
A currency pair is a quotation that shows the value of one currency in relation to another. It is written as “base/quote,” where the base currency appears first and the quote currency second. This pair indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency.
For example, in EUR/USD, EUR is the base and USD is the quote currency. If the rate is 1.1000, one Euro equals 1.10 US Dollars.
Currency pairs allow traders to speculate, hedge, and take advantage of global economic shifts. Each pair comes with unique levels of volatility, liquidity, and trading cost, so understanding these characteristics helps in managing risk and timing trades effectively. This knowledge also supports those using a regulated forex broker or a CFD trading broker, ensuring transparent pricing and fair execution.
Learning how to analyse and read different currency pairs is essential for mastering How to Read and Trade Currency Pairs.
Common currency pairs are the most traded in the forex market, often involving the US Dollar and another major global currency such as the Euro, Yen, Pound, Swiss Franc, or Canadian Dollar. Popular examples include EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF, AUD/USD, and NZD/USD. These major pairs usually have the tightest spreads, the highest liquidity, and the most stable trading conditions.
Keep learning with Eurotrader and explore How to Choose the Best Currency Pair to Trade to match your trading style and goals.
Many different currencies can be traded in the foreign exchange market, but the most actively traded are known as the major currency pairs. These currencies include the U.S. Dollar (USD), Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), British Pound (GBP), Swiss Franc (CHF), Canadian Dollar (CAD), and Australian Dollar (AUD). These seven currencies make up the majority of trade in the forex market and are usually the most liquid.
Major currency pairs all contain the US Dollar (USD) on one side, either on the base side or the quote side. The most common combinations are EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, and USD/CHF, but the other combinations are also popular. Among these, EUR/USD remains the most traded, influenced by major economic announcements from both Europe and the United States.
The other big pairs include AUD/USD, NZD/USD, USD/CAD, and other combinations. These pairs are less commonly traded than the majors, but they still offer plenty of trading opportunities. They are often influenced by news from their respective countries, as well as commodity prices and other factors. Many traders also engage in commodities trading online, where currency correlations with gold, oil, or metals can impact forex movements and pair dynamics.
Exotic currency pairs involve currencies from emerging or developing economies, often paired with a major one such as USD or EUR. Examples include MXN/JPY, ZAR/SGD, and HKD/INR. These pairs have higher spreads and volatility, offering potential for larger profits, but also increased risk. Traders must approach them with caution and strong risk management. Those exploring cryptocurrency trading online will notice similar volatility patterns, making risk control equally important across both markets.
Understanding currency pairs is fundamental to forex trading. Exchange rates move constantly, influenced by interest rates, market sentiment, and economic data. Traders must also monitor liquidity — how easily a currency can be bought or sold — and spreads, which vary between pairs depending on market conditions and broker pricing. Understanding these factors is also critical for CFD trading, where currencies, indices, and commodities can all be traded on margin through a single platform.
The value of a currency can be affected by many different factors, both political and economic. When it comes to a currency’s value, it is important to consider both internal and external factors.
Internally, a currency can be affected by factors such as:
Externally, a currency can be affected by factors such as:
These internal and external factors all have a direct effect on a currency, as they all affect the demand for a currency in the international market. A currency with a higher demand will be valued more highly than one with a lower demand.
At Eurotrader, we empower traders to understand currency movements and trade confidently. Whether you prefer CFD trading or direct forex trading through a regulated forex broker, our platform, tools, and educational resources are designed to help you grow your skills and reach your goals. Join Eurotrader today and take your trading to the next level.